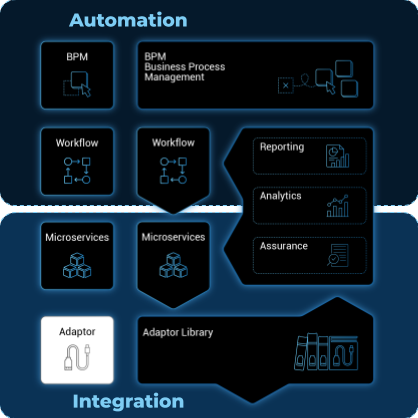
The adapters are the "drivers" that allow the main MSactivator™'s engine to seamlessly communicate with the Managed Entities for configuration assurance, event collection, et cetera.
Overview
The adapters are designed per vendor because they need to address the specifics of each vendor especially when the Managed Entitie does not provide a REST management API.
The MSactivator™ provides a library of device adaptors ready to use.
The libraries are implemented in PHP which makes extension and customization easy.
How to find, install, activate the adapters
The Adapters are packaged in the MSactivator™, in the "msa_dev" container, under /opt/devops/Openmsa_Adapters which is a git repository configured to point to github.
$ sudo docker-compose exec msa-dev bashMany other Adapters are available on the Adapters Github repository
The installation of an Adapter is covered in this documentation: How to install an Adapter
REST Generic adapter
The REST Generic adapter, available on Github will allow you to integrate most vendors that exposes a REST management interface API.
This adapter is included in the mini lab.
If you need to create a new vendor based on the REST Generic adapter, you can follow this guide in the next section
How to create a new vendor based on an existing adapter
Overview
Some adapters were designed to be generic in order to have little dependencies with a specific vendor.
This is the case for the REST and the Linux adapters.
-
The REST Generic adapter will let you quickly integrate a new managed entity with a REST based management API
-
The Linux Generic can be used for any Linux distribution or vendor model based on Linux
but you may want to also have the vendor name and entity model both appear in the list of supported vendor instead of REST/Generic or Linux/Generic.
Doing so will allow you to filter the microservice and deployment setting based on the vendor name and model name.
This will ease the organization of your integration files.
How to do it
Let’s assume that you want to add vendorA / modelX to the list of supported vendors.
You will need an access to the MSactivator™ CLI of the msa_dev container.
sudo docker-compose exec msa-dev bash
use msa_dev for MSactivator™ version 2.6 or older.
|
Create the new model in the Adapters github repository
If you followed the quickstart guide to install your instance of MSactivator™ the image msa_dev contains a clone of github.com/openmsa/Adapters
We are going to create the new model in this local repository. Using a git repository has several advantages such as using a working branch to track your changes and revert them if needed or contributing to the community by creating a pull request to submit your code.
Go to the repository
cd /opt/devops/OpenMSA_Adapters/
Go to the adapter definition directory and create a new folder for your new vendor model. By convention the folder name should be defined as <vendor name>\_<model name>
cd adapters mkdir -p vendorA_modelX/conf cd vendorA_modelX/conf
You need to create 2 configuration files to define this new model:
-
device.properties : define the adapter properties for UI display (msa-ui)
-
sms_router.conf : define the adapter config for the Core Engine (msa-sms)
| In the github repository you will find lot of doc and example about these files |
# VendorA / ModelX (1) manufacturer.id = 18082020 (2) manufacturer.name = VendorA model.id = 18082020 (3) model.name = ModelX obsolete = false
| 1 | any comment you find useful. |
| 2 | select a unique, numeric ID. Your current date it a good choice. |
| 3 | same as above. |
| the model ID and the manufacturer ID don’t have to be identical and you can have several models for the same vendor by using different model ID |
# VendorA / ModelX (1) model 18082020:18082020 (2) path rest_generic (3)
| 1 | any comment you find useful. |
| 2 | format: <manufacturer.id>:<model.id>. |
| 3 | the path to an existing adapter code (example: rest_generic or linux_generics). |
Update file owner
chown -R ncuser.ncuser /opt/devops/OpenMSA_Adapters/adapters/vendorA_modelX
Install and activate the new vendor
Exit the docker container msa-dev and restart the API container and the CoreEngine service
$ sudo docker-compose restart msa-api $ sudo docker-compose restart msa-sms
Verify your new vendor is available
Once the services have restart, you can connect to the UI to check that a new vendor/model is listed when you create a new managed entity.
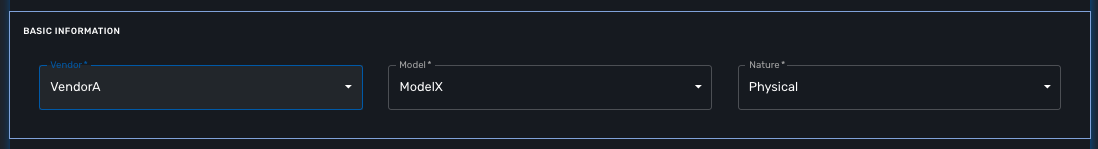
First, verify that you can create a new managed entity and try to activate it.
During the activation, you can monitor the logs of smsd daemon from the Core Engine and check that the adapter code being used is the one from rest_generic (or any other you may have set in sms_router.conf above)
Login to the CoreEngine container
$docker-compose exec msa-sms bash
Set the configuration log level to DEBUG
# tstsms SETLOGLEVEL 255 255
Monitor the logs with tail
# tail -F /opt/sms/logs/smsd.log
It should output something similar to that. You can verify that the managed entity activation is relying on the adapter code specified in sms_router.conf
2020/08/18:14:39:09:(I):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: analysing verb JSAPROVISIONING arg BLR129 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: arg: 1.2.3.4 aa aa 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: SMSSQL_GetSD current node name is msa, sdid = BLR129 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: Alloc SDINFO for BLR129 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: RUN script /opt/sms/bin/php/rest_generic/do_provisioning.php 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: LOAD_ONCE /opt/sms/bin/php/rest_generic/adaptor.php 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: LOAD_ONCE /opt/sms/bin/php/rest_generic/rest_generic_connect.php 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: LOAD_ONCE /opt/sms/bin/php/rest_generic/rest_generic_apply_conf.php 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: LOAD_ONCE /opt/sms/bin/php/rest_generic/rest_generic_connect.php 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: LOAD_ONCE /opt/sms/bin/php/rest_generic/provisioning_stages.php ... 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: script /opt/sms/bin/php/rest_generic/do_provisioning.php executed in 0.105652 seconds 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(D):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: free SDINFO for BLR129 2020/08/18:14:39:09:(I):smsd:BLR129:JSAPROVISIONING:: ends OK
Adapter SDK
The Adapter SDK is composed of a set of PHP scripts that implement an API This API exposes functions such as:
-
Asset management
-
Status polling
-
SshConnection
-
Provisioning
-
Update conf
-
Backup conf
-
Microservice commands (CREATE, READ, UPDATE, DELETE, IMPORT)
-
…
Custom commands
It is possible to implement new custom commands that will be callable from the MSactivator™ API (verb JSACMD MY_COMMAND).
Status polling
The MSactivator™ CoreEngine daemon in charge of polling the device for availability is polld.
Logs: /opt/sms/logs/sms_polld.log
By default, polling is using ping, and for scalability and performance reasons the polling mechanism is implemented in the C programming language.
This allows the MSactivator™ to poll several hundreds of managed entities per minute.
For the devices that don’t support ping, or in case the polling has to be customized, it is possible to implement a custom polling in a php script:
/opt/sms/bin/polld/<model>_polld.php
On Stormshield the connection to the device is tested as shown below
try
{
global $sms_sd_ctx;
netasq_connect();
netasq_disconnect();
}
catch (Exception $e)
{
netasq_disconnect();
return $e->getCode();
}
return SMS_OK;Asset management
The MSactivator™ CoreEngine can connect on a managed entity to fetch a set of predefined assets such as:
-
Firmware
-
Memory
-
CPU
-
…
The specific model script retrieves information (via CLI, snmp, REST calls…) into an array. The array is then passed to a specific callback in order to store the information in the database.
sms_polld_set_asset_in_sd($sd_poll_elt, $asset);It is also possible to extract custom assets. They will be stored in the database as a list of key values.
The asset mngt module uses regular expressions to extract the asset from the configuration.
These values are stored in a database that keeps the asset history.
The asset script is device specific and is located in:
/opt/sms/bin/polld/<model>_mgmt.php
Regexp:
$get_system_status_asset_patterns = array(
'firmware' => '@Version:\s+(?<firmware>.*)@',
'av_version' => '@Virus-DB:\s+(?<av_version>.*)@',
'ips_version' => '@IPS-DB:\s+(?<ips_version>.*)@',
'serial' => '@Serial-Number:\s+(?<serial>.*)@',
'license' => '@License Status: (?<license>.*)@',
);The regexp is executed against the result of the CLI : get system status.
Regexp:
$show_ver_asset_patterns = array(
'serial' => '@Processor board ID (?<serial>\S*)@',
'license' => '@oftware \((?<license>[^\)]*)\)@',
'firmware' => '@\), Version (?<firmware>[^,]*),@',
'model' => '@^(?<model>[^(]*) \(.*with \d+K/\d+K bytes of memory@',
'cpu' => '@^.* \((?<cpu>[^\)]*)\) processor@',
'memory' => '@with (?<memory>\d*K/\d*K bytes) of memory@',
);The regexp is executed against the result of the CLI show version.
Configuration management
Dialog with the managed entity
The following PHP scripts have to be created in the /opt/sms/bin/php/<model>/ directory.
This set of PHP scripts manages the dialog between the {produt_name} and the managed entity.
Provides access to the device for device connection and configuration update.
Manages the connection to the device (SSH, or REST, for example).
Microservice based configuration
PHP scripts to configure a device using objects:
Manages the OBMF specificities for the device.
Manages the main configuration methods for the managed entity (only update_conf() is used for objects).
Template based configuration
PHP scripts to configure a device using templates:
Generates and applies a configuration.
This task is also called automatically when the router configuration changes.
update_conf() should be enhanced to support configuration templates.
Provisioning
PHP scripts to do the initial provisioning of the device:
Generates and applies the initial configuration on the device. This is an asynchronous task, so a script must be provided to give an update on progress.
Describes all the provisioning stages. This is used to store the provisioning status into the database.
Provisioning action to lock the database for this device during the provisioning.
This is the initial connection test.
Add the device to the MSA local DNS.
Provisioning action to unlock the database for this device during the provisioning.
Other Features
Called by GUI (menu Monitoring → Get the running configuration).
Generate the staging configuration for the device (menu General → Staging).
Generate a backup of the device configuration.
Restore a configuration backup on the device.
Update the firmware of a device.
If a script is not present, the corresponding operation on the MSactivator™ will give the "Function not supported by the device" error.
Connectivity to the Devices
For the managed entities that expose a remote CLI based management interface the adapter API requires the implementation of a class that extends SshConnection.
SshConnection connection is defined in /opt/sms/bin/php/smsd/ssh_connection.php
SshConnection extends GenericConnection defined in /opt/sms/bin/php/smsd/generic_connection.php
SshConnection extends GenericConnection defined in /opt/sms/bin/php/smsd/generic_connection.php
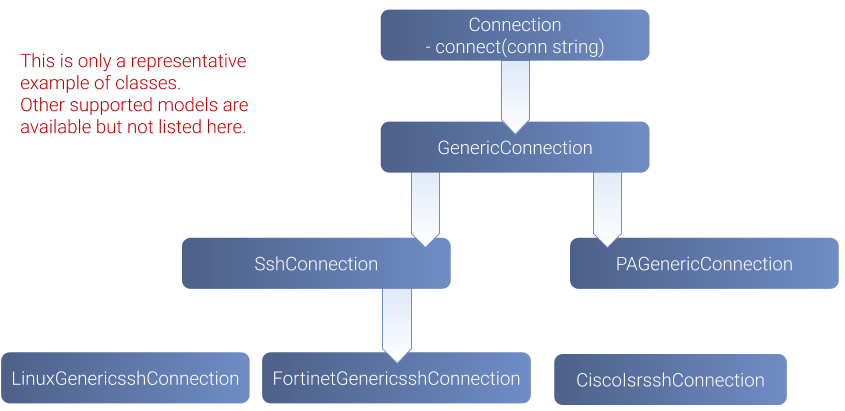
The class Connection
This class is always overridden by a generic connection. It defines functions such as the "get" and "set" attributes such as the prompt, the device IP (sd_ip_config) …
The function connect
It defines the main connect functions public function connect($connectString).
This function uses the PHP function proc_open to execute the connect command and opens file pointers for IO.
The disconnect closes the IO file pointers and leaves a clean state.
sendexpectone for sending a command to a device and getting the result back.
public function sendexpectone($origin, $cmd, $prompt='lire dans sdctx', $delay = EXPECT_DELAY, $display_error = true)Example (in Fortinet adaptor)
$buffer = sendexpectone(__FILE__ . ':' . __LINE__, $this, 'get system status', '\#');The class GenericConnection
This class implements a constructor that initiates a class attribute.
Device information is read by calling the function get_network_profile().
get_network_profile is defined for each device in a PHP file located in:
/opt/sms/spool/php_db_data/<device_id>.php
This PHP file is an “image” of the device configuration as stored in the database.
This design allows a quick and easy access to device configurations such as IP, credentials, interface name, SNMP community, customer ID …
The class SshConnection
It implements the function do_connect() that uses the function connect() from the class Connection:
parent::connect("ssh –p 22 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no…It uses the function expect() to check that SSH connectivity is OK (by checking that the result contains “Permanently added”).
The class SshKeyConnection
Allows public/private keys via SSH authentication with the device.
Fortiweb WAF on AWS requires this kind of authentication.
Other examples
/opt/sms/bin/php/linux_generic/linux_generic_connect.php
Used in do_update_conf.php
$ret = linux_generic_connect();Implementation of ‘Update Configuration’
Base operation for implementing:
-
The initial provisioning
-
The template-based configuration
-
The Microservice CREATE/UPDATE/DELETE operation
Implemented by do_update_conf.php
Can be called directly by the MSactivator™ CoreEngine API, it is an asynchronous process, its status can be monitored.
Managed entity activation (initial provisioning)
The MSactivator™ executes a set of steps to activate the device.
The steps can be customized to do additional operations.
Defined in provisioning_stages.php
$provisioning_stages = array(
0 => array('name' => 'Lock Provisioning', 'prog' => 'prov_lock'),
1 => array('name' => 'Initial Connection', 'prog' => 'prov_init_conn'),
2 => array('name' => 'Initial Configuration', 'prog' => 'prov_init_conf'),
3 => array('name' => 'DNS Update', 'prog' => 'prov_dns_update'),
4 => array('name' => 'Unlock Provisioning', 'prog' => 'prov_unlock'),
5 => array('name' => 'Save Configuration', 'prog' => 'prov_save_conf'),
)Configuration backup/restore
Based on the verb GETSDCONF (see save_router_conf.sh) which is implemented by do_get_sd_conf.php for each device.
The implementation will vary depending on the vendor.
Fortinet uses TFTP and CLI execute restore config tftp. Cisco ISR first tries to SCP to flash and to TFTP and then reboots.
Connectivity fallback mechanism
By default, the device adaptor uses secure protocols to communicate with the devices (SSH or TFTP).
When these protocols fail (the device doesn’t support them or firewall restrictions – which might be unlikely), there is a fallback mechanism to protocols such as Telnet or TFTP.
in cisco_isr_connect.php
Microservice implementation
The implementation of the functions CREATE/READ/UPDATE/DELETE/IMPORT is specific to the vendor.
| this is especially true for the IMPORT. |
CREATE/READ/UPDATE/DELETE are using the functions to apply conf, this is similar to the configuration update.
IMPORT needs to be aware of the device configuration structure.
It is necessary to provide a unified GUI to build the import but with devices that have different data models.
| for REST based managed entities, the IMPORT is usually generic since the response is formatted in XML or JSON (cf. rest_generic) |
The MSactivator™ CoreEngine API
As well as named verbs, these commands can be used to interact directly with the MSactivator™ CoreEngine from the CLI.
The can also be executed with a REST API:
HTTP Request: /sms/verb/{verb}/{deviceId}
Method: POST
| Parameter Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
verb |
String |
the command (JSAPROVISIONING, JSCHECKPROVISIONING, JSAUPDATECONF,…) |
deviceId |
String |
the database ID of the managed entity |
| COMMAND | |
|---|---|
JSAPROVISIONING |
Initial provisioning |
JSCHECKPROVISIONING |
Check initial provisioning status |
JSAUPDATECONF |
Update configuration |
JSSTAGING |
Staging |
JSGETSDCONF |
Get router running configuration |
JSGETCONF |
Get router generated |
The verbs are associated to specific PHP do_<verb>.php:
tstsms JSGETSDCONF UBI132
This will retrieve the running configuration of the device and use the implementation of do_get_running_conf.php.
Operation status feedback
During operations done by the MSactivator™ CoreEngine, especially the asynchronous ones, the status of the ongoing operation can be set for the user by the PHP scripts. How to update the status depends on the operation.
Set provisioning status for a provisioning stage.
sms_bd_set_provstatus($sms_csp, $sms_sd_info, $stage, $status, $ret, $next_status, $additionalmsg)Set the update status of the configuration update of an equipment.
sms_set_status_update($sms_csp, $sdid, $error_code, $status, $e->getMessage())This has covered various aspects of Adapter development. If you have further questions, please contact info@ubiqube.com for more information.