The BPM editor is a web based UI for designing BPM processes.
Overview
The MSactivator™ provides a web based user interface editor for designing BPM (Business Process Model).
BPM are sitting at the top of the automation layer and the editor will allow you to create BPM in a codeless way.
BPM design
To create a new BPM from the developer portal, click on "+ Create" from the swimlane "BPM Library."
You can also browse through the existing BPM by clicking on "See more".
| you need to select a sub-tenant to see the BPM. |
BPMN elements
The MSactivator™ BPM engine supports the following BPMN elements:


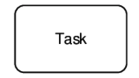



| Bear in mind that a gateway is not a task! You have to determine facts and needs before reaching a gateway. |
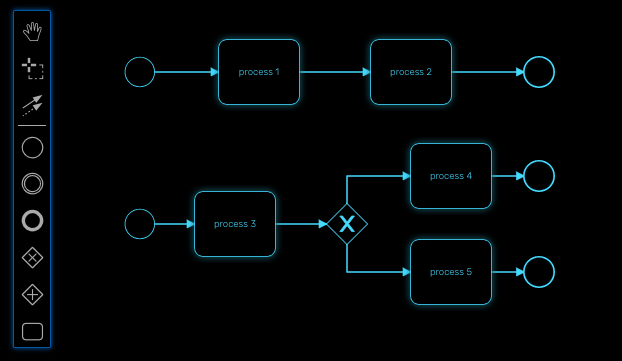
Parallel gateway (AND)
Gateways can also be used to model concurrency in a process.
The most straightforward gateway to introduce concurrency in a process model is the Parallel Gateway, which allows forking into multiple paths of execution or joining multiple incoming paths of execution.
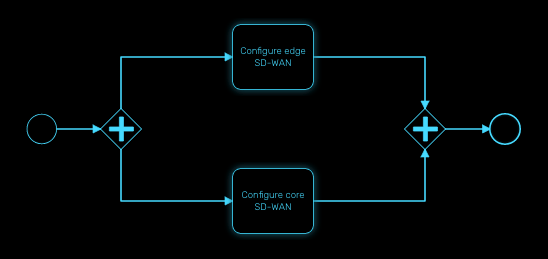
The functionality of the parallel gateway is based on the incoming and outgoing sequence flow(s):
-
fork: all outgoing sequence flows are followed in parallel, creating one concurrent execution for each sequence flow.
-
join: all concurrent executions arriving at the parallel gateway wait at the gateway until an execution has arrived for each of the incoming sequence flows. Then the process continues past the joining gateway.
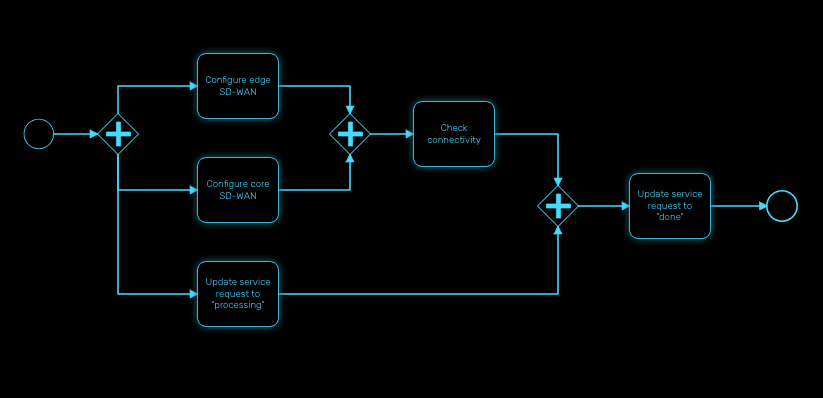
Note that a parallel gateway does not need to be ‘balanced’ (i.e., a matching number of incoming/outgoing sequence flows for corresponding parallel gateways). A parallel gateway will simply wait for all incoming sequence flows and create a concurrent path of execution for each outgoing sequence flow, not influenced by other constructs in the process model. So, the following process is legal in MSactivator™:
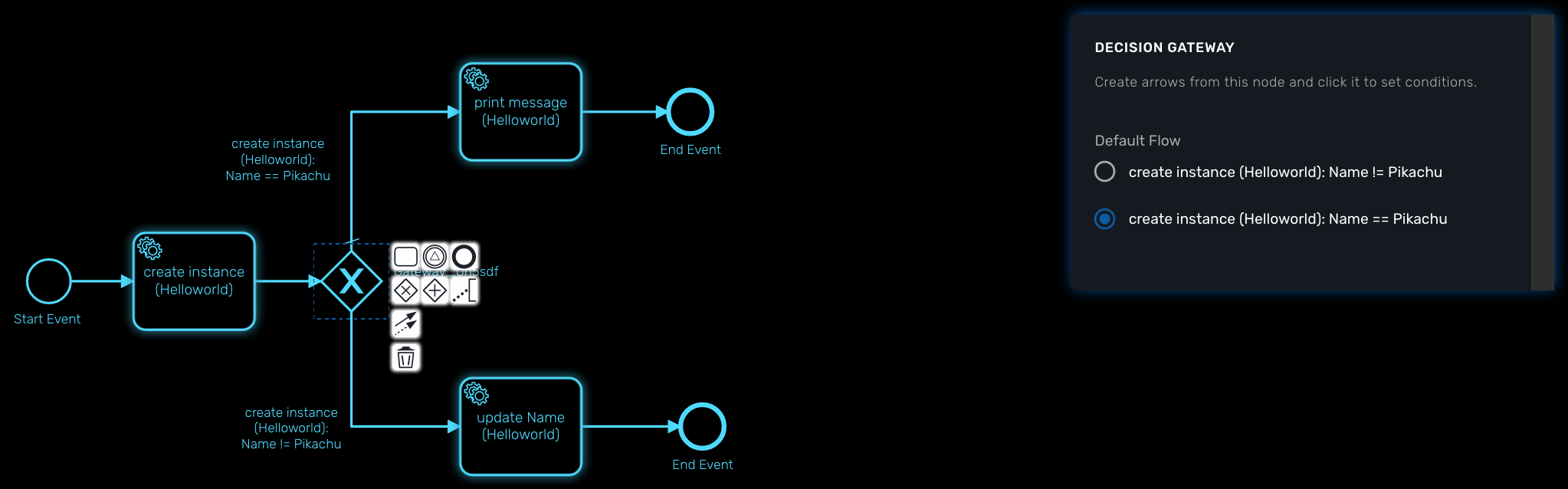
Decision gateway (XOR)
The XOR gateway will let you model a decision in the process.
When the execution arrives at this decision gateway, all outgoing sequence flows are evaluated in the order in which they have been defined. The sequence flow whose condition evaluates to ‘true’ is selected for continuing the process.
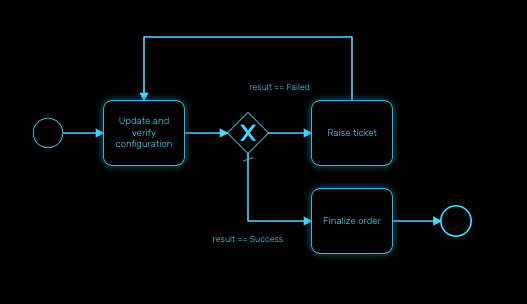
To configure the gateway, you need to select the outbound link from the gateway, choose the inbound task and configure the condition to transition to the next BPM task.
Configure a decision gateway
To configure a decision gateway, you need to configure each of its outbound links and select one of the outbound link to be the default flow.
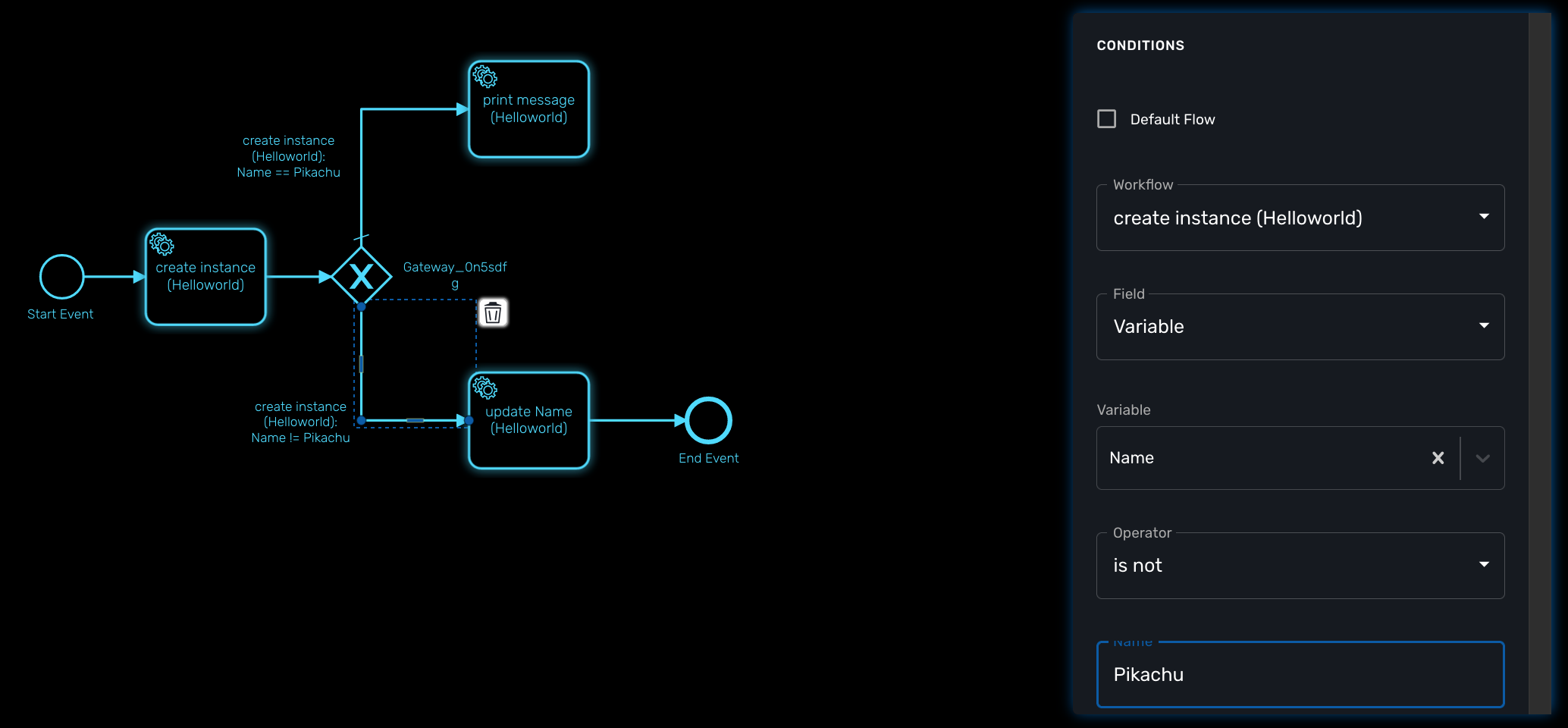
Default flow
Click on the decision gateway ans select the default flow of the process when there is not suitable condition based on the result of the inbound task.
Workflow
For each outbound link, select the inbound workflow that will be used as the condition source for the link.
Field
Select the field to use to test the condition. Field can be "Variable" or "Result Status".
With "Variable", you can choose one of the workflow variable and test its value for the decision.
With "Result Status", the decision will depend on the execution status of the workflow.
Design a BPM process
Create a new BPM
Click on "Create" to create a new BPM editor.
Use your mouse to add tasks and link them together.
| A BPM process must have a StartEvent and an EndEvent. |
| Only one executable BPM process can be specified in a BPM definition. |
You can save your BPM at anytime and edit it later. When you save you BPM, you need to select a sub-tenant.
| A BPM is associated to a single sub-tenant. |
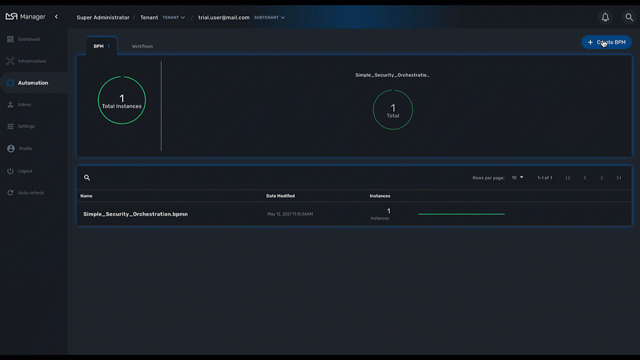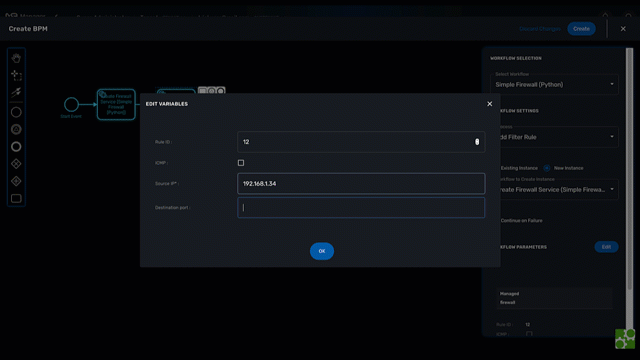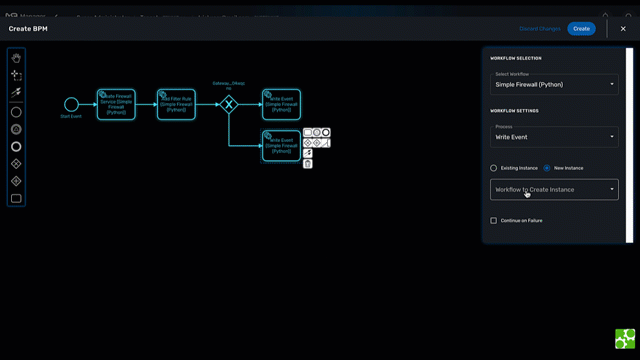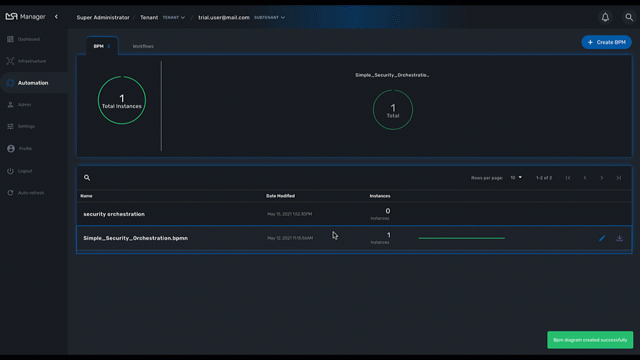
Connecting workflows and processes
Select an executable task to see the list of workflows (based on the sub-tenant selected), then select a process and provide its input parameters.
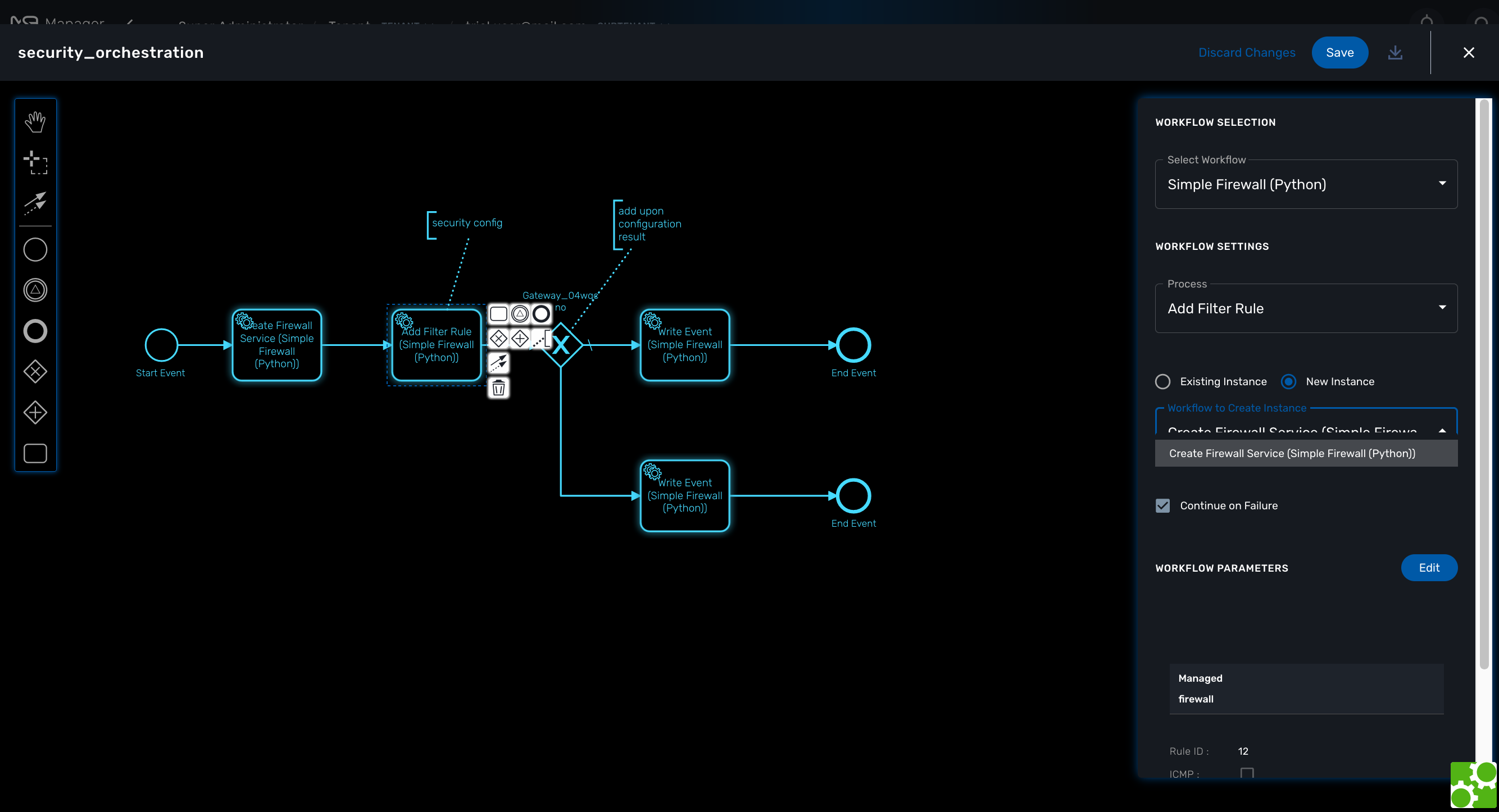
If the process you select in a BPM task is a "UPDATE" process (see Workflow design for more details), you’ll have the possibility to select either an existing Workflow instance or use a new instance created by one of the previous BPM task.
This is extremely useful for BPM designers for chaining tasks together.
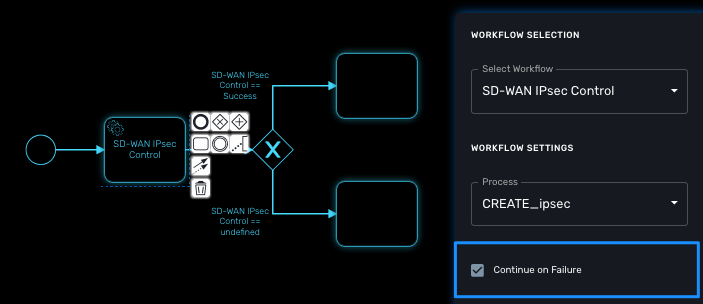
Execution flow control
By default, the BPM execution will stop whenever the associated workflow process execution fails but you may need to make sure that the BPM continues to execute despite the failure. This is typically the case when there is a decision gateway where execution is routed based on the status of the process execution.
To allow the BPM process to continue executing after a workflow process execution fails, you need to edit the BPM task and check "Continue on Failure."
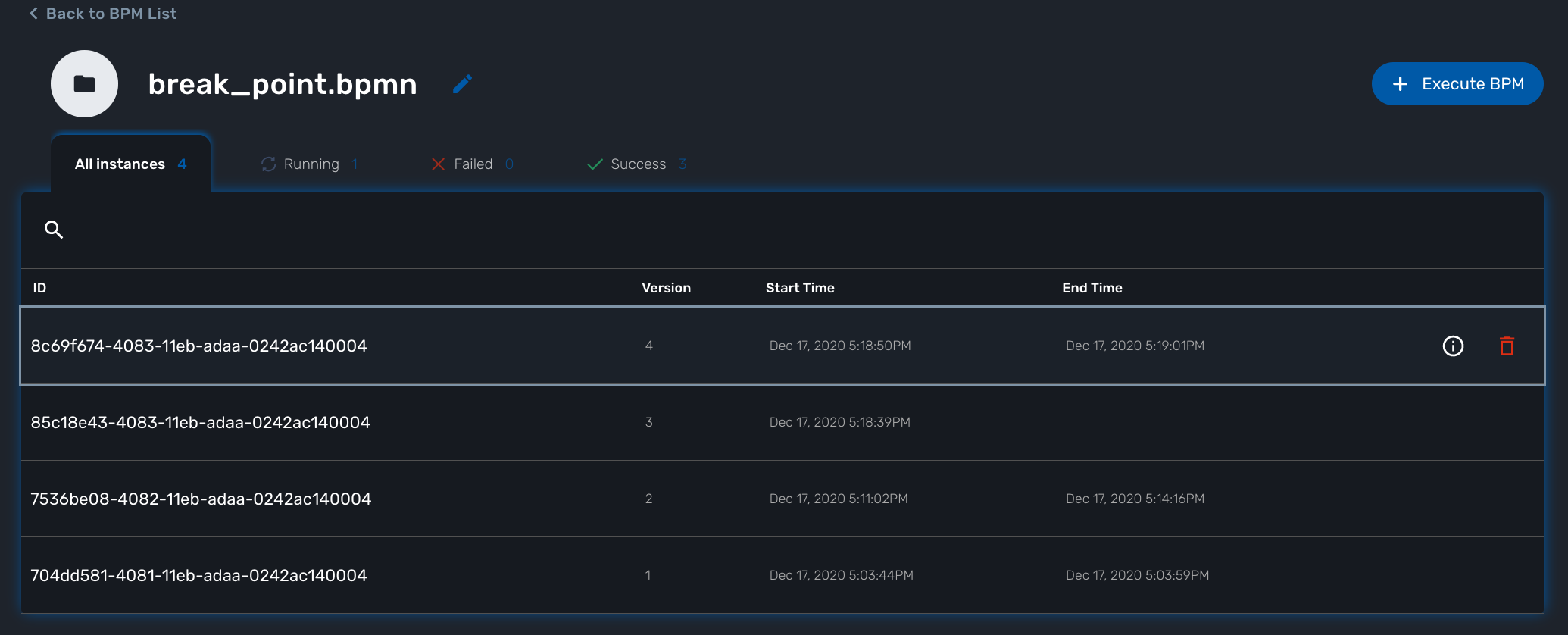
Execution breakpoint
With the execution breakpoint you can create pauses in the BPM flow execution. The BPM process will run, stop and wait for the user to select the breakpoint symbol and click "Continue BPM" to resume it’s execution.
Breakpoints can be used for debugging a complex BPM process without triggering all the workflow and doing a step by step execution. It can also be used to organise a complex BPM into several part and allow for manual validation of each intermediate steps.
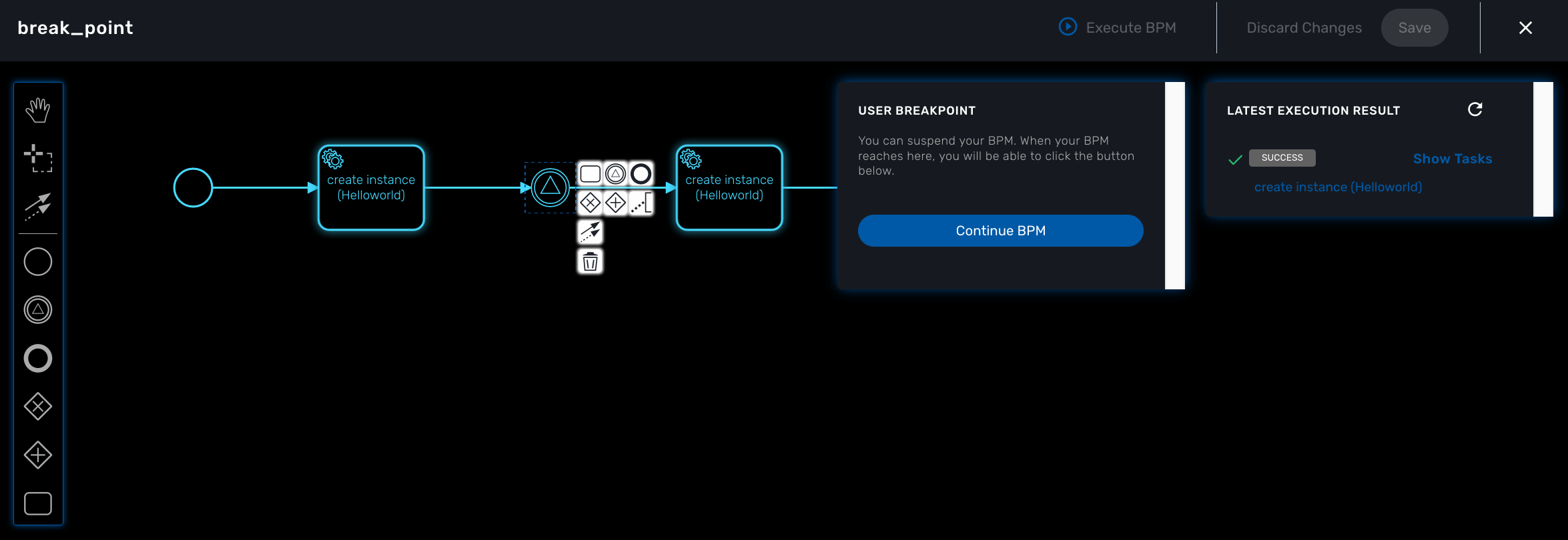
Execution tracking
The BPM engine will start executing the BPM tasks one by one and the status of the current workflow process execution will be updated live in the view "LATEST EXECUTION RESULT" while the detail of the process execution will be displayed.
![]()
BPM instances management
BPM are associated to a subtenant in a way which is very similar to workflows, you can manage the instances of BPM executions.
For instance, if you executed a BPM with a breakpoint, you don’t need to leave the BPM execution screen open. You can trigger the execution, close the screen and later, select the instance and open it.