You can use the the microservice editor UI to create or update a microservice.
To create or edit a microservice you can go to the "Integration" section and select the Microservice tab
CLI microservice implementation
The Microservice API is made of several functions that can be implemented. It is not mandatory to implement all the functions, this will depend on your requirements and can be done incrementally.
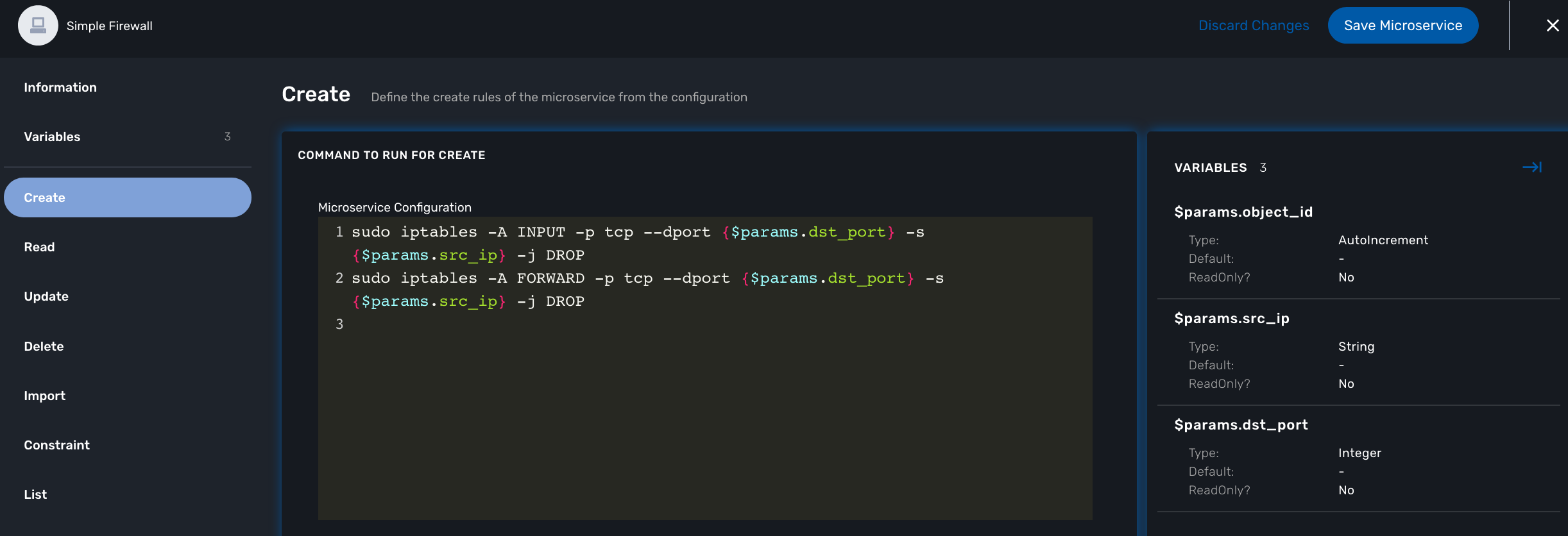
The functions Create, Update and Delete
Create and Update
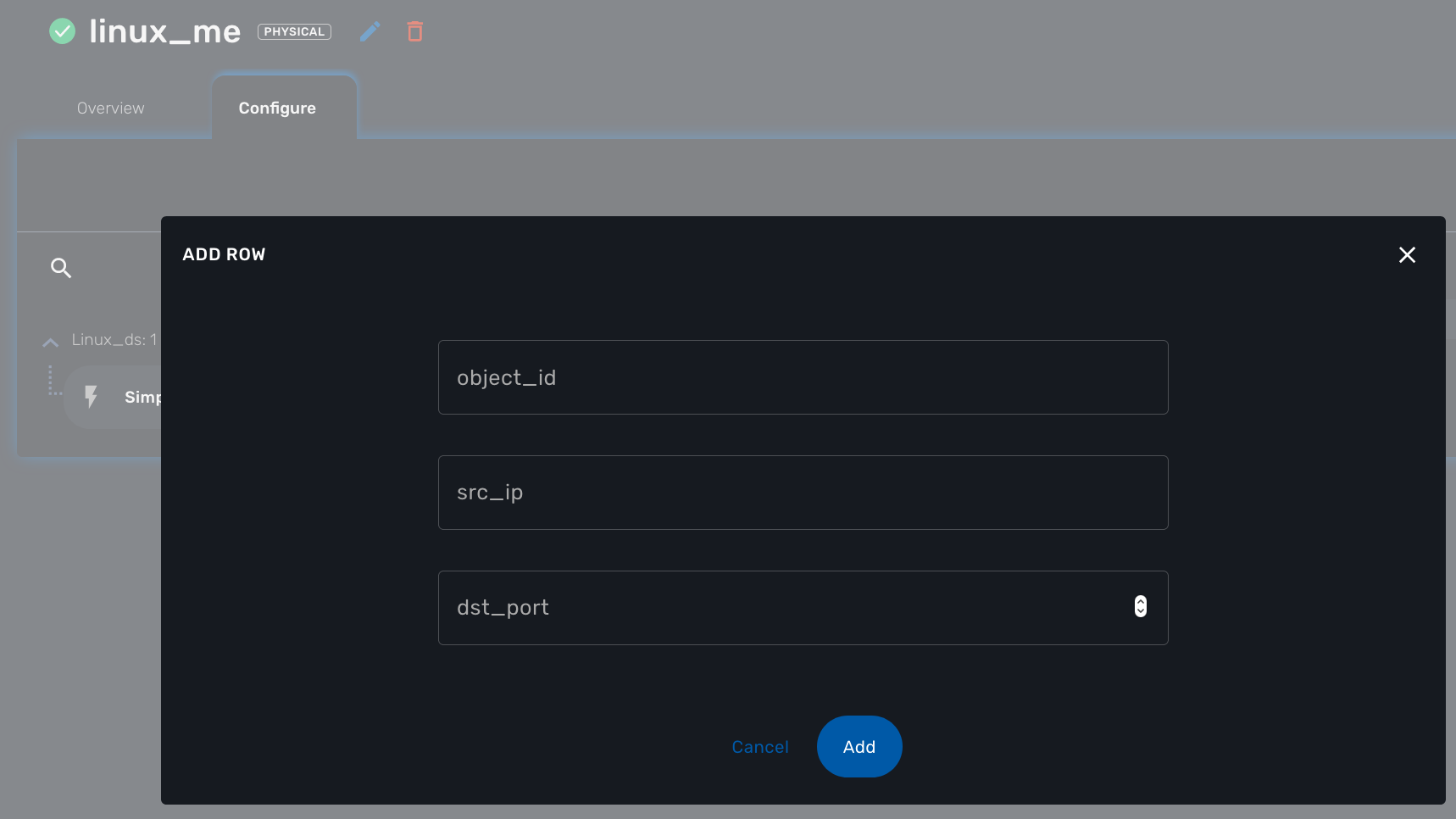
The CLI commands to create or delete an iptable rule to allow or block a port and an IP are:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport <PORT TO BLOCK> -s <IP TO BLOCK> -j DROP sudo iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp --dport <PORT TO BLOCK> -s <IP TO BLOCK> -j DROP
this is how it would be implemented in the Create function of the Microservice
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport {$params.dst_port} -s {$params.src_ip} -j DROP
sudo iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp --dport {$params.dst_port} -s {$params.src_ip} -j DROP
As you can see the parameters are prefixed with $params. and this is the reason why the variable editor section will automatically add $params. to the variable.
The implementation of the Update will be similar and will of course depend on the CLI syntax.
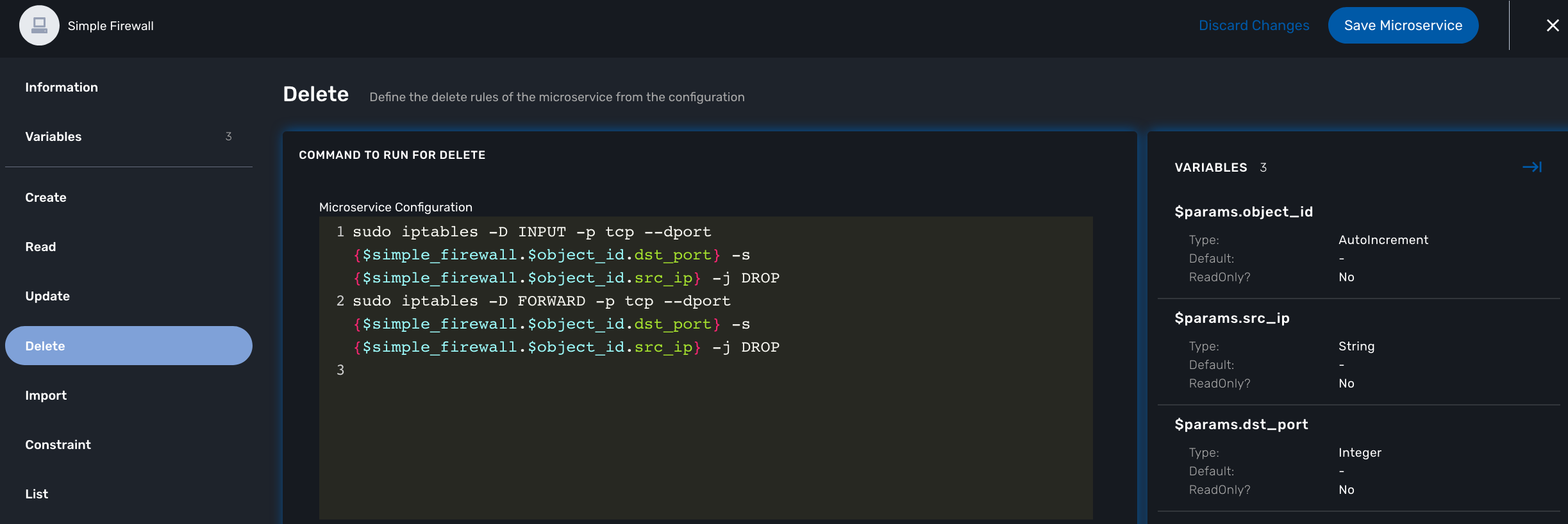
Delete
The deletion of the iptables INPUT and FORWARD rules is executed with the CLI command below:
sudo iptables -D INPUT -p tcp --dport <PORT TO BLOCK> -s <IP TO BLOCK> -j DROP sudo iptables -D FORWARD -p tcp --dport <PORT TO BLOCK> -s <IP TO BLOCK> -j DROP
This will be implemented as:
sudo iptables -D INPUT -p tcp --dport {$simple_firewall.$object_id.dst_port} -s {$simple_firewall.$object_id.src_ip} -j DROP
sudo iptables -D FORWARD -p tcp --dport {$simple_firewall.$object_id.dst_port} -s {$simple_firewall.$object_id.src_ip} -j DROP
The syntax {$simple_firewall.$object_id.dst_port} provides a way to access the Microservice variable values in the MSactivator™ configuration database.
The convention is as follow:
{$<MICROSERVICE NAME>.$object_id.<VARIABLE NAME>}
In our case:
-
MICROSERVICE NAME ⇒ simple_firewall
-
VARIABLE NAME ⇒ dst_port
-
MICROSERVICE NAME is the name of the Microservice file without the .xml extension.
The function Import
This regex will extract the firewall parameter and store them in the database
@(?<object_id>\d+) DROP tcp -- (?<src_ip>([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3})[^:]+:(?<dst_port>\d+)@
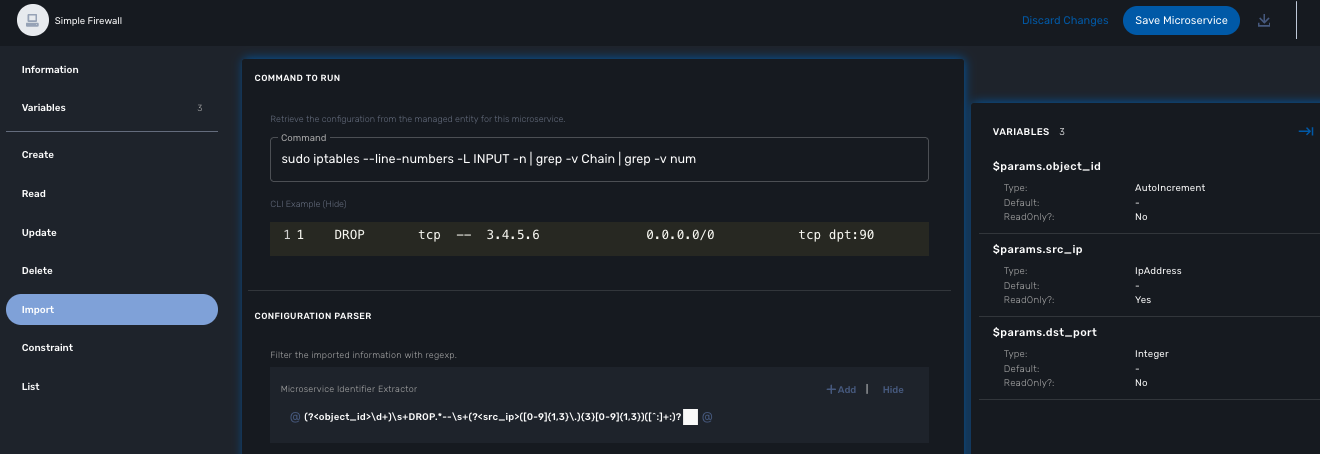
the variable object_id is a mandatory parameter and will be used to identify the Microservice instance in the database.
|
Testing the microservice
The Microservice is ready to be tested.
Make sure that you can add and delete a policy rule, that it’s reflected on the Linux firewall, and that the parameters are also properly synchronised after a call to Create or Delete.
You can also add some iptables rules manually on the Linux CLI and run a configuration synchronization to make sure that your manual changes are properly imported.
Import function: tips and examples
Below you’ll find some example of CLI based configuration and the regex that can be used to extract the variables.
These are only provided as example and you may have to modify them to match you needs.
To help with testing and validating your regular expression, there are many online tools. We, at UBiqube, usually use this one: https://regexr.com/3bhgg
Example 1 : Fortigate, get the syslogd3 config
CLI command: how full-configuration log syslogd3 setting
result:
config log syslogd3 setting
set status enable
set server "91.167.210.90"
set mode udp
set port 514
set facility local7
set source-ip ''
set format default
end
Here is the Import function implementation to extract the object_id, the status, the server IP and the port.
| config | regex | instance key | value |
|---|---|---|---|
config log syslogd3 setting |
config log (?<object_id>\S+) setting |
syslogd.syslogd3.object_id |
syslogd3 |
set status enable |
\s*set status (?<syslogd3_status>\S+) |
syslogd.syslogd3.syslogd3_status |
enable |
set port 514 |
\s*set port (?<syslogd3_port>\d+) |
syslogd.syslogd3.syslogd3_port |
514 |
set server "91.167.210.90" |
\s*set server "(?<syslogd3_server_ip>[^"]+)" |
syslogd.syslogd3.syslogd3_server_ip |
91.167.210.90 |