Smarty templates
The Smarty templates are used to generate output using variables and control structures like if/then/else conditional branches or for/each loops.
The output is used to configure the managed entities or retrieve data from the database.
Parameter substitution in microservice
Whether you are developing a CLI or and XML (REST) based microservice, the CoreEngine will rely on parameter substitution to generate the configuration or the call to the REST API.
The parameters, coming from the web UI or the REST API are passed to the template engine as a JSON payload.
For ClI microservices, the parameters, extracted from the JSON payload will be used to generate the piece of configuration to apply to the managed entity (this is the role of the adapter).
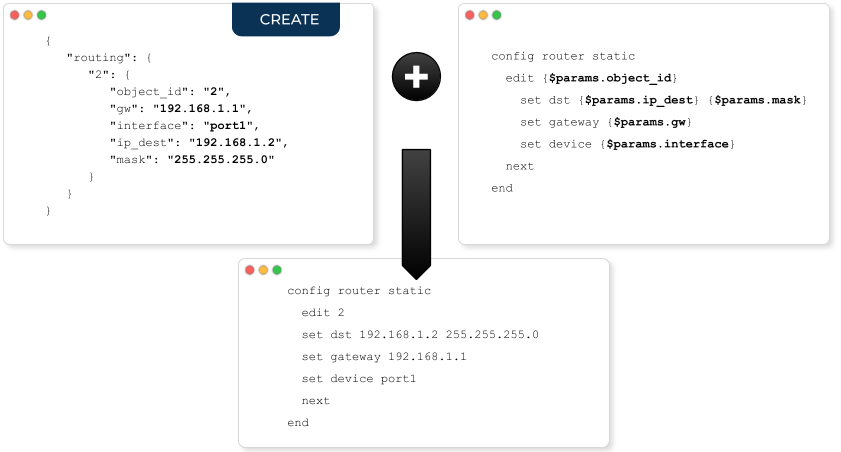
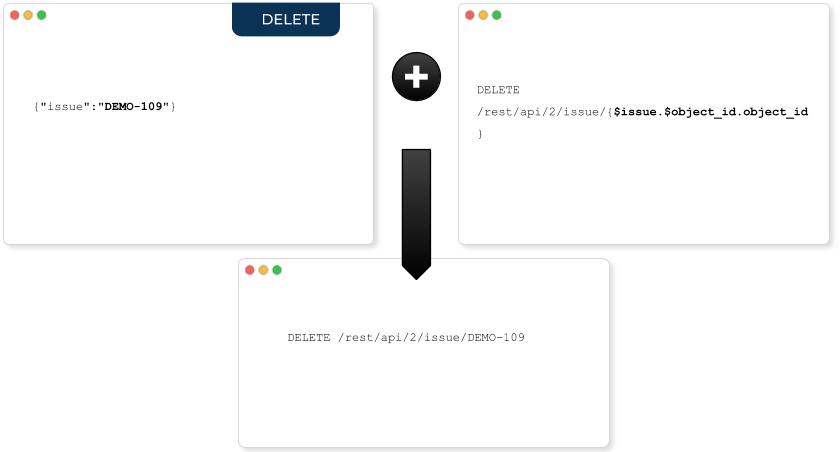
For XML/REST, the parameters are used to build the REST API call, either by updating the path and/or by updating the payload
Variables
From database
For an object object_name, the instance instance_id can accessed with the syntax
{$object_name.instance_id}
Object fields can be accessed via
{$object_name.instance_id.field_name}
Array values can be accessed with the syntax
{$object_name.instance_id.array_name.array_index}
Special case of object_id
{$object_id}
can also be used. It corresponds to the object ID given in the JSON parameter object.
The {$object_id} variable can also be used to retrieve an object instance from the database.
{$object_name[$object_id|object_id]}
is the instance of object_name corresponding to the object ID given in parameters.
Smarty has a specific meaning for the '.' dot character, so it is not allowed in $object_id variable. In order to solve this issue, it is better to use {$params.object_id} instead of {$object_id} when generating the configuration.
In order to reference the value of another object, the Smarty modifier '|object_id' can be use.
Example:
v2.0/subnets/{$subnets[$params.object_id|object_id].uuid}
will fetch the uuid parameter of the 'subnets' object having $params.object_id id.
Control Structures
Control structures are used to generate output using complex data, like list of objects, or optional parts.
Conditionals
{if},{elseif},{else}
{if} statements in Smarty have much the same flexibility as PHP if statements, with a few added features for the template engine. Every {if} must be paired with a matching {/if}. {else} and {elseif} are also permitted. All PHP conditionals and functions are recognized, such as ||, or, &&, and, is_array(), etc.
The following is a list of recognized qualifiers, which must be separated from surrounding elements by spaces. Note that items listed in [brackets] are optional. PHP equivalents are shown where applicable.
| Qualifier | Alternates | Syntax Example | Meaning | PHP Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
== |
eq |
$a eq $b |
equals |
== |
!= |
ne, neq |
$a neq $b |
not equals |
!= |
> |
gt |
$a gt $b |
greater than |
> |
< |
lt |
$a lt $b l |
less than |
< |
>= |
gte, ge |
$a ge $b |
greater than or equal |
>= |
⇐ |
lte, le |
$a le $b |
less than or equal |
⇐ |
=== |
$a === 0 |
check for identity |
=== |
|
! |
not |
not $a |
negation (unary) |
! |
% |
mod |
$a mod $b |
modulous |
% |
is [not] div by |
$a is not div by 4 |
divisible by |
$a % $b == 0 |
|
is [not] even |
$a is not even |
[not] an even number (unary) |
$a % 2 == 0 |
|
is [not] even by |
$a is not even by $b |
grouping level [not] even |
($a / $b) % 2 == 0 |
|
is [not] odd |
$a is not odd |
[not] an odd number (unary) |
$a % 2 != 0 |
|
is [not] odd by |
$a is not odd by $b |
[not] an odd grouping |
($a / $b) % 2 != 0 |
telephony-service
{if isset($params.ntp_server_ip_address) && $params.ntp_server_ip_address != ''}
ntp-server {$params.ntp_server_ip_address}
{/if}
{if isset($params.maximum_ephones) && $params.maximum_ephones != ''}
max-ephones {$params.maximum_ephones}
{/if}
{if isset($params.maximum_dial_numbers) && $params.maximum_dial_numbers != ''}
max-dn {$params.maximum_dial_numbers}
{/if}
{if isset($params.source_ip_address) && $params.source_ip_address != ''}
ip source-address {$params.source_ip_address} port {$params.source_port} {if isset($params.secondary_ip_address) && $params.secondary_ip_address != ''} secondary {$params.secondary_ip_address} {/if}
{/if}Loops
{foreach},{foreachelse}
{foreach} is used to loop over an associative array as well a numerically-indexed array, unlike {section} which is for looping over numerically-indexed arrays only.
The syntax for {foreach} is much easier than {section}, but as a trade off it can only be used for a single array. Every {foreach} tag must be paired with a closing {/foreach} tag.
Attribute Name |
Type |
Required |
Default |
Description |
from |
array |
Yes |
n/a |
The array you are looping through |
item |
string |
Yes |
n/a |
The name of the variable that is the current element |
key |
string |
No |
n/a |
The name of the variable that is the current key |
-
Required attributes are from and item.
-
{foreach} loops can be nested.
-
The from attribute, usually an array of values, determines the number of times {foreach} will loop.
-
{foreachelse} is executed when there are no values in the from variable.
telephony-service
{foreach from=$params.tftp_load item=tftp}
load {$tftp.phone_type} {$tftp.firmware_file_name}
{/foreach}Sorting
Use the smarty function 'sortby_typed' to sort arrays by key.
'sortby_typed' take a list of comma separated keys with a type (int or string) for each one.
{foreach $params.access_list|@sortby_typed:"acl_seq_number:int" as $acl} (1)
{$acl.acl_seq_number} {$acl.acl_rule} {$acl.acl_protocol} {$acl.acl_src}
{/foreach}| 1 | sort by the key 'acl_seq_number' and convert the key values to integer |
Variable assignment
Local variable
Under certain circumstances it is necessary to use a local temporary variable to generate the output.
{assign}
{assign} is used for assigning template variables during the execution of a template.
Attribute Name |
Type |
Required |
Default |
Description |
var |
string |
Yes |
n/a |
The name of the variable being assigned |
value |
string |
Yes |
n/a |
The value being assigned |
!
{assign var='sdid' value=$SD->SDID}
{foreach from=$VOIP_PROFILE->SD_list.$sdid->MAIL_BOX_list item=mbox}
!
voicemail mailbox owner {$mbox->MBOX_USERNAME}
login pinless any-phone-number
end mailbox
{/foreach}
!Microservice variable
It is also possible to assign a value to a microservice variable.
This is only possible in the post-import section.
{if isset($params.syslogd_server_ip) && $params.syslogd_server_ip != ""}
{assign_object_variable var="_syslogd_server_ip" value="{$params.syslogd_server_ip}"} (1)
{/if}| 1 | assign the value of $params.syslogd_server_ip to $params._syslogd_server_ip |
Common problems
The templates are extracted from the XML definition files, and evaluated with Smarty. Some behavior must be known prior to developing templates.
XML non supported characters
Templates within XML definition files must not contain characters like < or >. You’ll get an error:
Bad format for local file due to XML parsing error.
<command name="CREATE">
<operation>
you can't "write" if ({$foo} < 1) in your templates
</operation>
</command>Templates must be embedded into a <[CDATA[ ]]> tag to avoid most of the problems of non-supported characters.
<command name="CREATE">
<operation><[CDATA[
you can "write" if ({$foo} < 1) in your templates
]]></operation>
</command>Extra line break and space characters
The templates reflects what is written within the <operation> and </operation> tags, that’s why it is recommended to write
 When a Smarty command like {if} {foreach}, or also an ending tag like {/if} {/foreach}, is immediately followed by a line break, then this line break is REMOVED by Smarty.
This does NOT apply to variables.
When a Smarty command like {if} {foreach}, or also an ending tag like {/if} {/foreach}, is immediately followed by a line break, then this line break is REMOVED by Smarty.
This does NOT apply to variables.
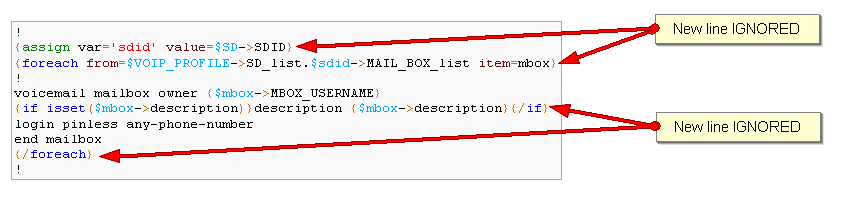
In this case the
{if} ... {/if}
The line should have been split.
!
{assign var='sdid' value=$SD->SDID}
{foreach from=$VOIP_PROFILE->SD_list.$sdid->MAIL_BOX_list item=mbox}
!
{if isset($mbox->description)}
description {$mbox->description}
{/if}
voicemail mailbox owner {$mbox->MBOX_USERNAME}
login pinless any-phone-number
end mailbox
{/foreach}
!Sometimes the line cannot be split, the solution is to either add a space character at the end of the line, if it remains correct for the configuration, or add an extra new line (one line left blank).

Syntax errors
The Smarty syntax is very strict, for example an error in the template
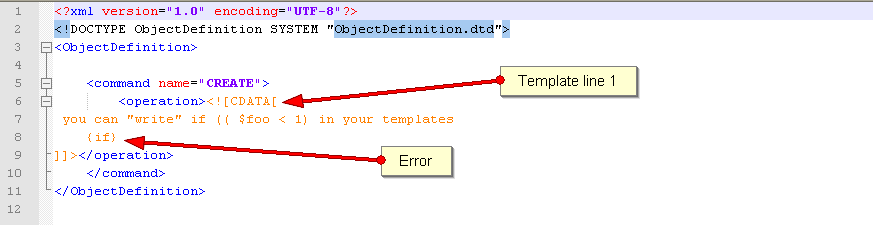
will return
Operation Failed
Currently, the only way to find the root cause is to check the file
/opt/sms/logs/smsd.log
An example of an error found in the log
2011/08/12:12:28:42:(D):smsd:ZTD66206:JSCALLCOMMAND:: Managing object test
2011/08/12:12:28:42:(D):smsd:ZTD66206:JSCALLCOMMAND:: compute file /opt/fmc_repository/CommandDefinition/CISCO/MyTemplates/test.xml for key test
2011/08/12:12:28:42:(D):smsd:ZTD66206:JSCALLCOMMAND:: ELEMENT CREATE found
2011/08/12:12:28:42:(E):smsd:ZTD66206:JSCALLCOMMAND:: PHPERROR: [256] Smarty error: [in var:2313098ec4aae945b1a201eb153cf778 line 3]: syntax error: 'if' statement requires arguments (Smarty_Compiler.class.php, line 1270) error on line 1093 in file /opt/sms/bin/php/smarty/Smarty.class.phpThis indicates that in the file
CommandDefinition/CISCO/MyTemplates/test.xml
for the command
CREATE
an error occured in the 3rd line of the template
syntax error: 'if' statement requires arguments
Usage of the {$object_id} variable
The {$object_id} variable is used to reference objects into the database and is used as a variable name in Smarty in the template resolution.
When the parameters are passed to the engine the JSON payload is:
{"interface":{"Interface-Service-engine0/0":{"ip_address":"1.2.3.4"}}}
The variables values are:
-
{$object_id}⇒ "Interface-Service-engine0/0" -
{$params.ip_address}⇒ "1.2.3.4"
When writing a template {$object_id} can be used in expressions like {$interface.$object_id.ip_address} to retrieve database values.
The CREATE template looks like:
<command name="CREATE">
<operation>
<![CDATA[
interface {$object_id}
{if isset($params.dot1qtrunk) && $params.dot1qtrunk == 'Yes'}
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport mode trunk
{/if}
{if isset($params.vlan_id) && $params.vlan_id != ''}
encapsulation dot1Q {$params.vlan_id}
{/if}
{if isset($params.ip_address) && $params.ip_address != ''}
ip address {$params.ip_address} {$params.subnet_mask}
{/if}
{if $object_id|stristr:"Ethernet" && !$object_id|stristr:"."}
{if isset($params.enable_nbar) && $params.enable_nbar != '' && $params.enable_nbar == 'Yes'}
ip nbar protocol-discovery
{/if}
{if isset($params.enable_media_type) && $params.enable_media_type != '' && $params.enable_media_type == 'Yes'}
max-reserved-bandwidth 100
media-type sfp
{/if}
{if isset($params.description) && $params.description != ''}
description {$params.description}
{/if}
...
no shutdown
!]]>
</operation>
</command>Skip the parsing of the {$ } structure
Normally, the {$ } structure is used in the microservices template to specify the variables to be parsed by the Smarty templating engine (ex: {$parms.my_variable}) but in some case, you might need this structure to be ignored by the parser because it is part of the actual configuration to build for the managed entity.
This is where you need to use the keywords ldelim (left delimiter )and rdelim (right delimiter).
For example consider the following pattern in the "Microservice Configuration" section of the REST based Microservice definitions:
"subUnit": "{$v_vni-0-0_WAN-1__unit}"
Here we want to use the '{' and '}' characters in their literal values and have to specify not to be parsed. We can do this by replacing '{' with '{ldelim}' and replacing '}' with '{rdelim}' and hence for the line mentioned above we have to change it as shown below:
"subUnit": "{ldelim}$v_vni-0-0_WAN-1__unit{rdelim}"