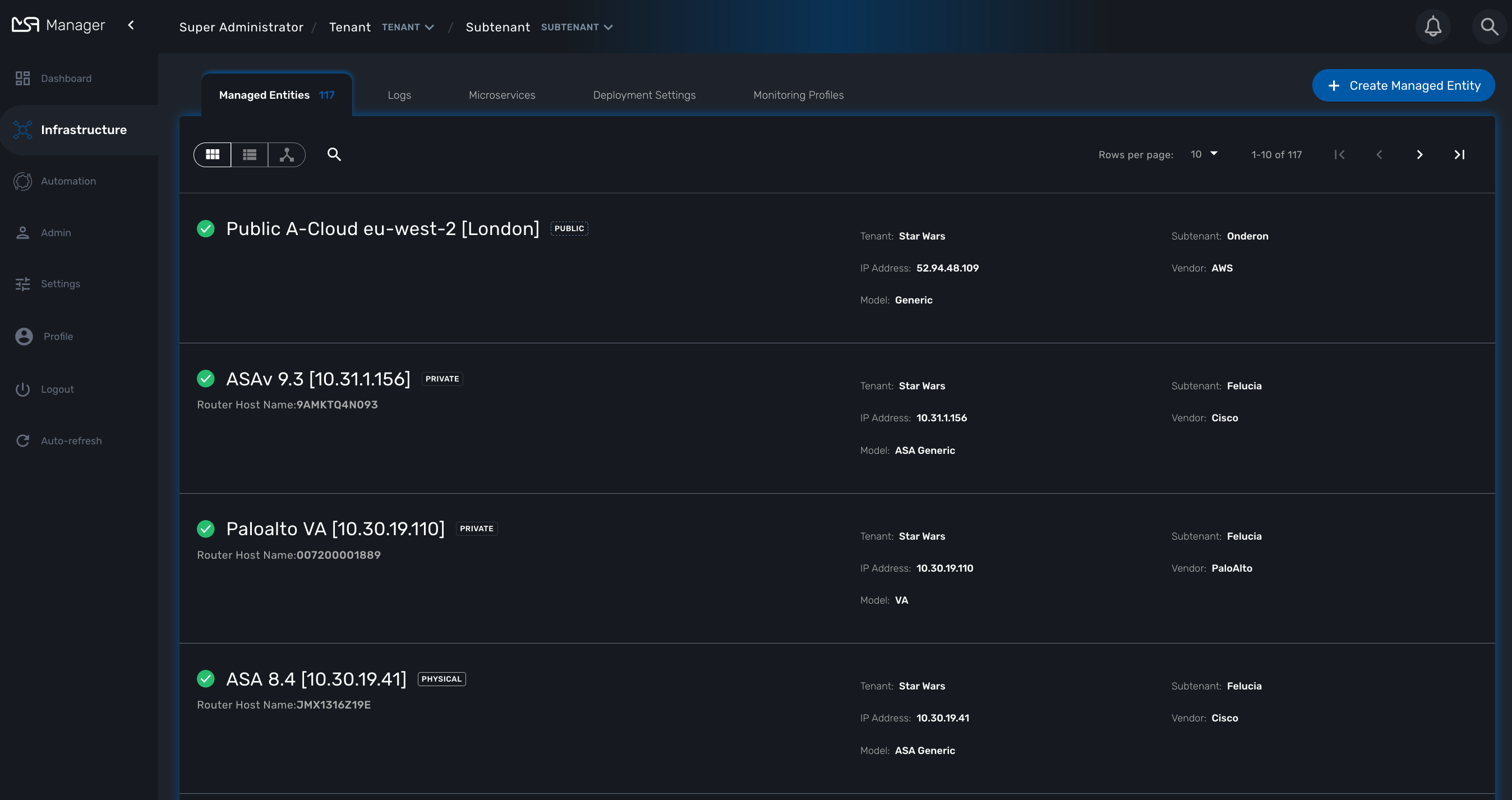
Managed Entities are the logical representation of any element of an infrastructure such as network devices, security devices, VNF, VIM,…
Overview
In order to become a manageable entity, an entity such as a router, a firewall or any other network function or element, physical or virtual, has to be created and activated in the MSactivator™.
These entities are managed in the "Infrastructure" section of the MSactivator™.
You can create a new managed entity or browse to an existing one and manage it.
This screen provides 3 types of view and you can switch between the detailed view, the compact view or the topology view.
Create, update and activate a managed entity
To create a managed entity, click the "+ Create Managed Entity" button on the managed entity screen.
This will bring you to the form to create a managed entity.
The fields marked with a * are mandatory to create a managed entity. If a tenant or customer is selected on the global filter, then they will be pre-populated in the form. Otherwise a tenant and customer must be selected.
The selections in the "Vendor" and "Model" fields will determine the fields displayed in the "Management Information" and "Advanced Information" sections. Different managed entity types have different associated variables that are used in their provisioning and operation.
| The selection of the vendor and model will determine the Adapter that will be used by the CoreEngine for configuration and assurance. It’s important to select an adapter that is compatible with the managed entity model. Once a managed entity is created, it is not possible to change the model, the managed entity will have to be recreated. |
The managed entity creation form can be closed by pressing the "X" button in the top bar. Any data entered into the fields will be preserved for when the user returns to the form. Clicking the "Discard Changes" button will display a confirmation prompt. If the user accepts the form state will be reset.
The update form can be accessed by clicking the pencil icon on the managed entity Listing page or on the managed entity Detail page.
Managed entity fields
These are the fields available when creating a managed entity. Some are mandatory and this is made explicit by the * on the web form.
| All of these values are stored in the database and available to use by the Microservices, the Workflow, the API and the Adapters. |
Tenant and subtenant
Only available when creating a managed entity, you can’t change this value once the managed entity is created. If you selected the wrong tenant or subtenant you will have to recreate the managed entity.
Basic information
This will select the adapter the MSactivator™ CoreEngine will use for configuring and monitoring the managed entity
The nature of the managed entity is an additional information that will help you organize your infrastructure into physical devices and virtual (private or public) ones
Administrative information
The name is a free text field that you can use to identify your managed entity.
| Although the value uniqueness is not enforced by the MSactivator™ data model, it is very common to use a hostname for the name field. |
Management information
This is the IP address the MSactivator™ will use to manage and monitor the entity.
| hostname or FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) is not supported. |
You can optionally set the management interface name here. When set, the CoreEngine will attempt to use to poll the management interface traffic with SNMP.
The hostname of the managed entity.
The hostname is an optional field, it is used when syslog analytic is enabled for the managed entity in order to match the incoming syslog with a managed entity. It can also be used, if needed, in the adapter for various management reasons.
$network = get_network_profile(); (1)
$sd = &$network->SD;
$hostname = $sd->SD_HOSTNAME; (2)| 1 | read the managed entity data from the database |
| 2 | get the value of the hostname |
The management port is set to 22 by default and is used as is by most CLI command based adapters but for REST API adapters you’ll have to set it to the correct value.
Advanced information
Set the SNMP community configured on the actual managed entity.
Optionally set the monitoring port if it is not the default one (161)
Check to collect syslogs and optionally analyse the syslogs. The syslogs will be parsed and stored in the Elasctisearch cluster.
| log analytics must be enabled for SNMP trap monitoring. |
Provide the credential to authenticate to the managed entity.
The authentication is done at the adapter layer whenever it is required.
Managed entity activation
A managed entity can be activated by selecting "Activate" from the list of "Actions" at the top right of the managed entity screen.
This will show a form that takes the variables such as management IP, username and password that will be used in the activation. These fields may be pre-populated by the values given in the create form. If the variables are updated they will be used for that particular activation but will not be persistent.
When the activation is started the dialog shows the progress of the managed entity activation. This will update as the activation progresses and will show whether the activation succeeds or fails.
| the activation of the managed entity is executed by the adapter for this managed entity model. |
Overview screen
The overview screen is the main screen you will see when browsing to a managed entity
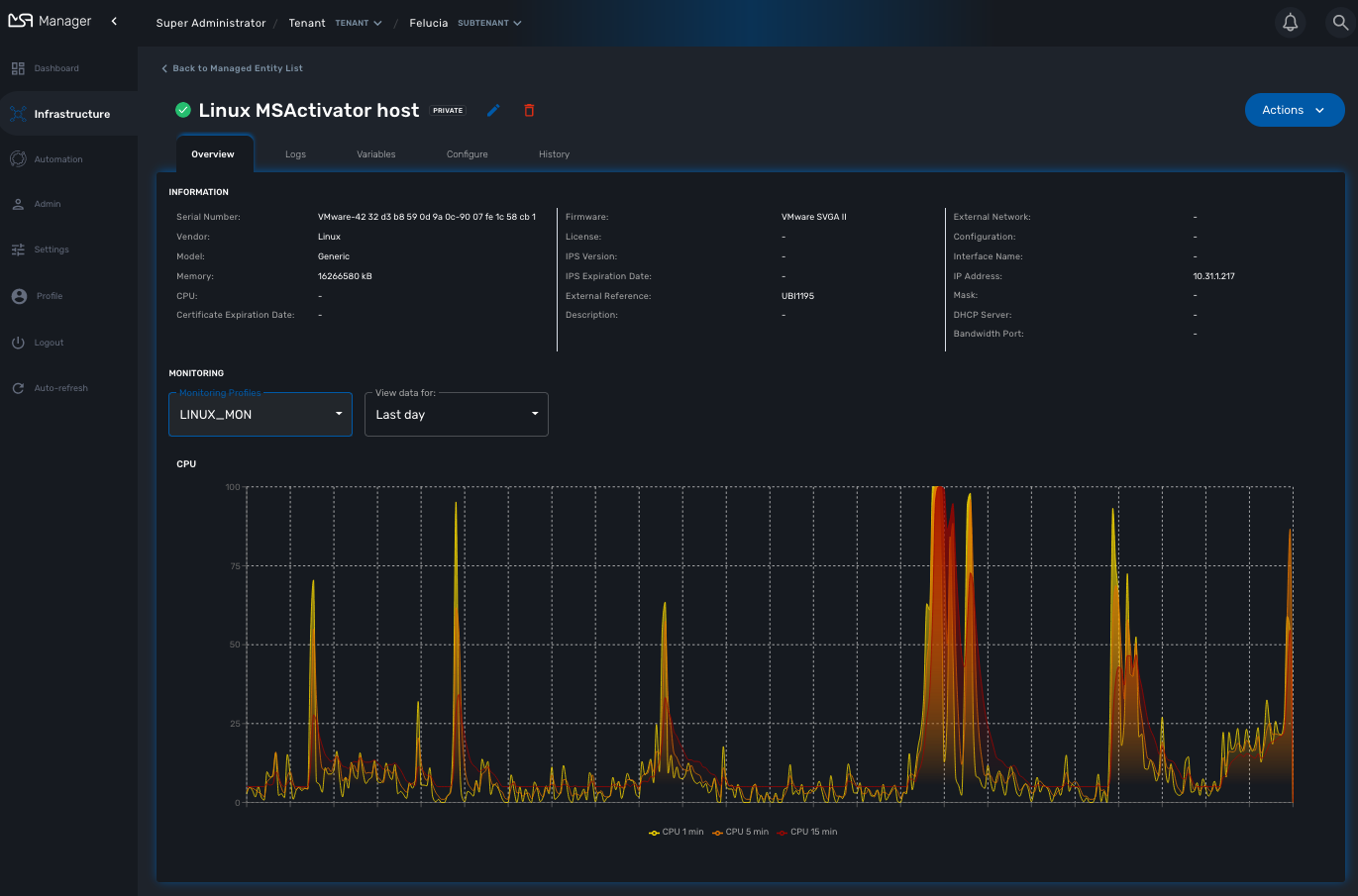
The managed entity overview screen is used to display the details of the selected entity.
You can reach this screen either by searching for a managed entity with the search field at the top right of the screen, or by selecting an entity from the managed entities list.
Asset information
The information such as the serial number, firmware, memory … are retrieved dynamically by the adapter once the entity is activated.
Monitoring information
By default there are 3 graphs that are displayed in the monitoring section of the overview screen:
-
the availability of the managed entity
-
the sysuptime of the managed entity
-
the network traffic of the management interface
Availability
A graph, based on ICMP requests (1/min) issued by the CoreEngine container msa_sms to the management interface of the managed entity, shows the latency and TTL information.
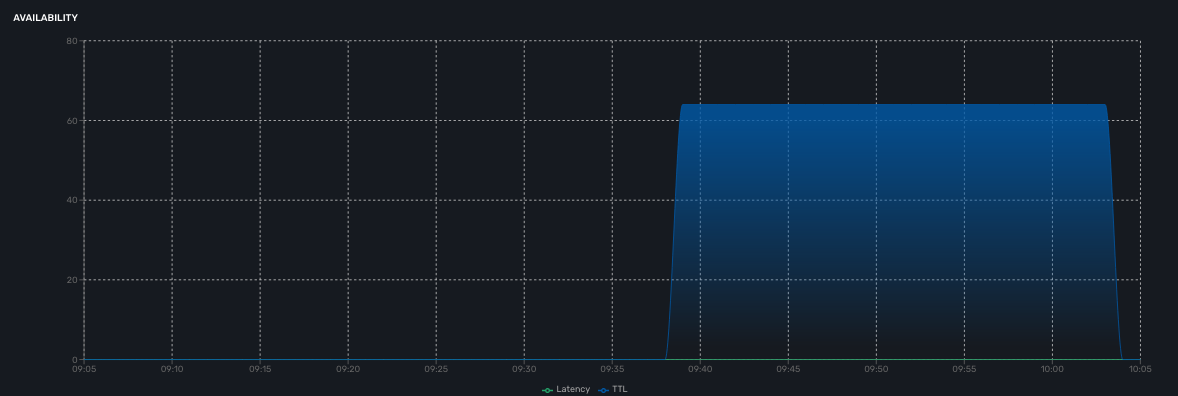
When the connectivity fails, a event VNOC-1-IPDOWN is generated by the CoreEngine and indexed in Elasticsearch log index.
An alarm can be configured based on this event.
When the connectivity is restored, a event VNOC-1-IPUP is generated and can also be used to generate an alarm.
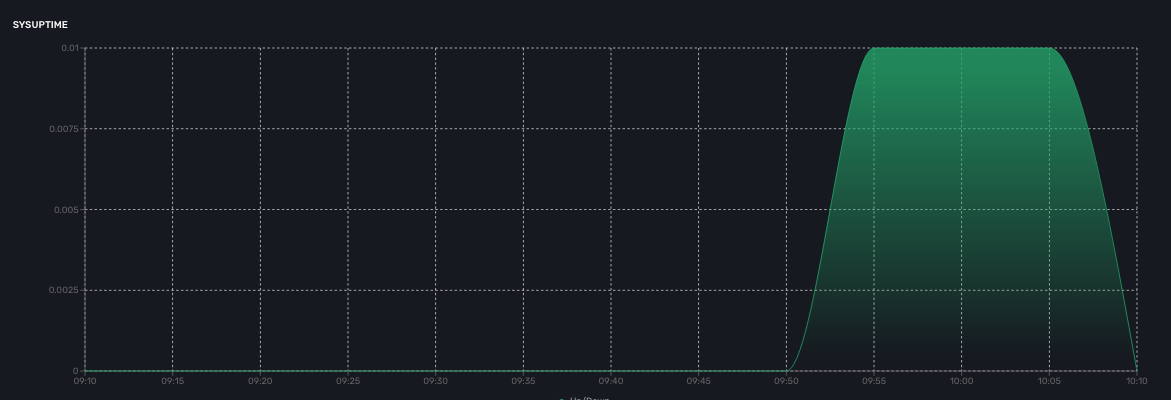
Sysuptime
The sysuptime (System Uptime) is collected by the CoreEngine with SNMP. You need to allow SNMP requests on the managed entity and configure the SNMP community for the managed entity.
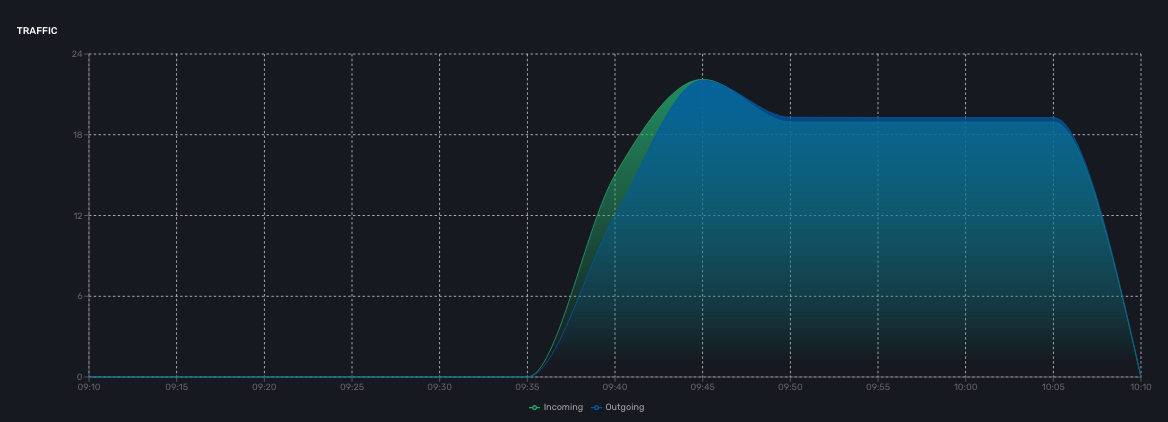
Traffic
The ingress and egress traffic of the management interface may be automatically collected provided that you have configured the management interface name in the managed entity configuration form.
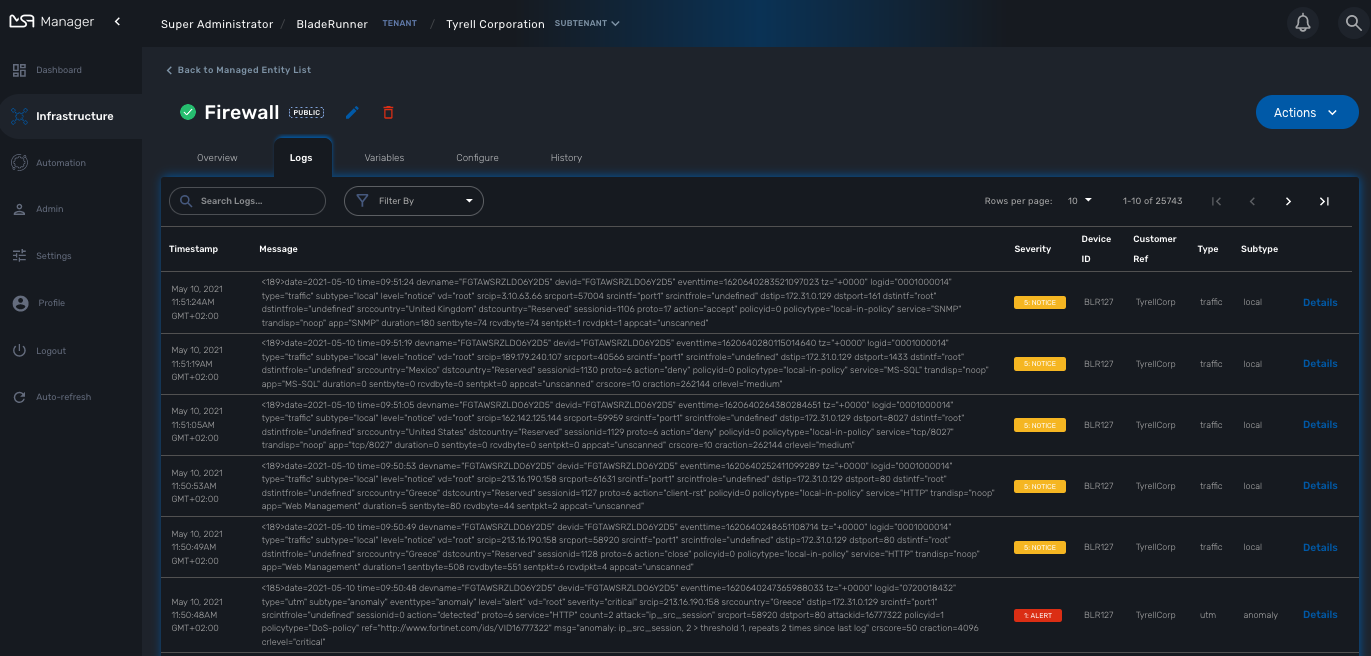
Logs
Logs, internal events and threshold crossing events are listed in the tab "Logs"
In order to view and search for the syslogs, you need to activate syslogs collecting and log analytics in the managed entity configuration form. You also need to make sure that the actual managed entity is properly configured to send it’s logs to the MSactivator™
Configuration variables
In addition to the UI fields, it is also possible to create custom additional configuration variable to a managed entity. Configuration variables offer a convenient way to extend the data model of the managed entity without any core product customization.
A configuration variables is a key/value couple stored in the database, associated to a managed entity.
Once a configuration variable is set on a managed entity, it is available to the microservices and the device adapter but it can also simply be used to add additional administrative information to a managed entity.
To create a configuration variable, click on the "Actions" menu on the top right of the managed entity screen and select "Create Variable".
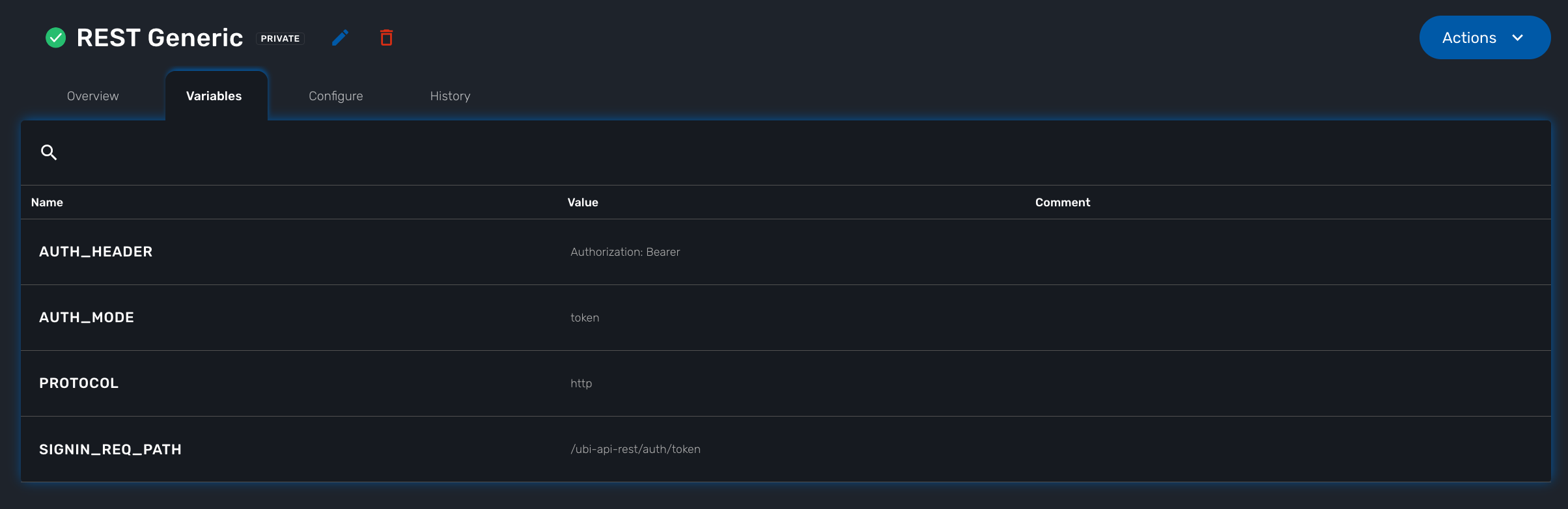
The REST generic adapter uses configuration variables to customize its behavior and adapt itself to the various type of REST API (BASIC auth vs. Token auth, HTTP vs. HTTPS,…)
$network = get_network_profile(); (1)
$sd = &$network->SD;
if (isset($sd->SD_CONFIGVAR_list['PROTOCOL'])) {
$protocol = $sd->SD_CONFIGVAR_list['PROTOCOL']->VAR_VALUE; (2)
}| 1 | read the managed entity data from the database |
| 2 | get the value of the configuration variable PROTOCOL |
In a microservice, you can reference any configuration variable with the syntax {$CONFIG_VAR_NAME}.
In a Import function, you can use a configuration variable to make the command to run on the device more flexible.
sho access-lists ACL-CUST{$CUSTOMER_REF} (1)
| 1 | make the name of the ACL depend on a configuration variable CUSTOMER_REF |
To read or set these configuration variables, you can use the REST API GET /variables/{deviceId}/{name} and PUT /variables/{deviceId}/{name}. This is useful for all your integration use cases or you can use the workflow from the library.
Configuration
Managed entities can be configured with microservices. To access the microservice console, click on the tab "Configure" on the managed entity screen.
In order to be able to use one or several microservices to configure a managed entity, the microservices must be associated to the managed entity via deployment settings.
Once associated to the managed entity, you can navigate to the managed entity tab "Configure" to access the microservice configuration console.
On the left menu of the console, you can see the list of the microservices that are associated to the current managed entity with the deployment setting.
Synchronization with the managed entity
In order to import the configuration from the actual managed entity into the MSactivator™ configuration database, you need to click on the link "Synchronize with Managed Entity".
This will call the CoreEngine and run the Import of each of the microservice.
The Import function may not always be implemented (this depends on the design of the microservice), therefore, the CoreEngine will simply skip these microservices.
Once the synchronization is done, the console will display the microservice instance, one by line, for each microservice.
In order to ensure that the configuration stored in the database is exactly reflecting the actual configuration of the managed entity, the microservice instances, specific to the current managed entity, are deleted from the database before the actual import can start.
Configuration of the managed entity
You can create a new microservice instance by selecting a microservice on the left menu and clicking "+ Add Row" and providing the input parameters to configure.
The input parameters are defined in the microservice "Variable" section.
| "+ Add Row" is only available when the Create function of the selected microservice is implemented. |
To update or delete a microservice instance, you need to select the row and click on "Edit" or "Remove".
| "Edit" or "Remove" actions are only available if the Update or the Delete functions of the microservice are implemented. |
Once you have updated your microservice, you can either click on "Discard Changes" or "Apply Changes".
"Discard Changes" will remove all the orders that where stacked and stored in memory.
"Apply Changes" will unstack all the orders and pass all the orders that were stacked to the CoreEngine configuration daemon. The configuration daemon will process the order, build the configuration and apply it to the managed entity.
History
The MSactivator™ maintains a configuration history database that allows you to track the configuration changes that occurred on a managed entity and execute some backup/restore actions
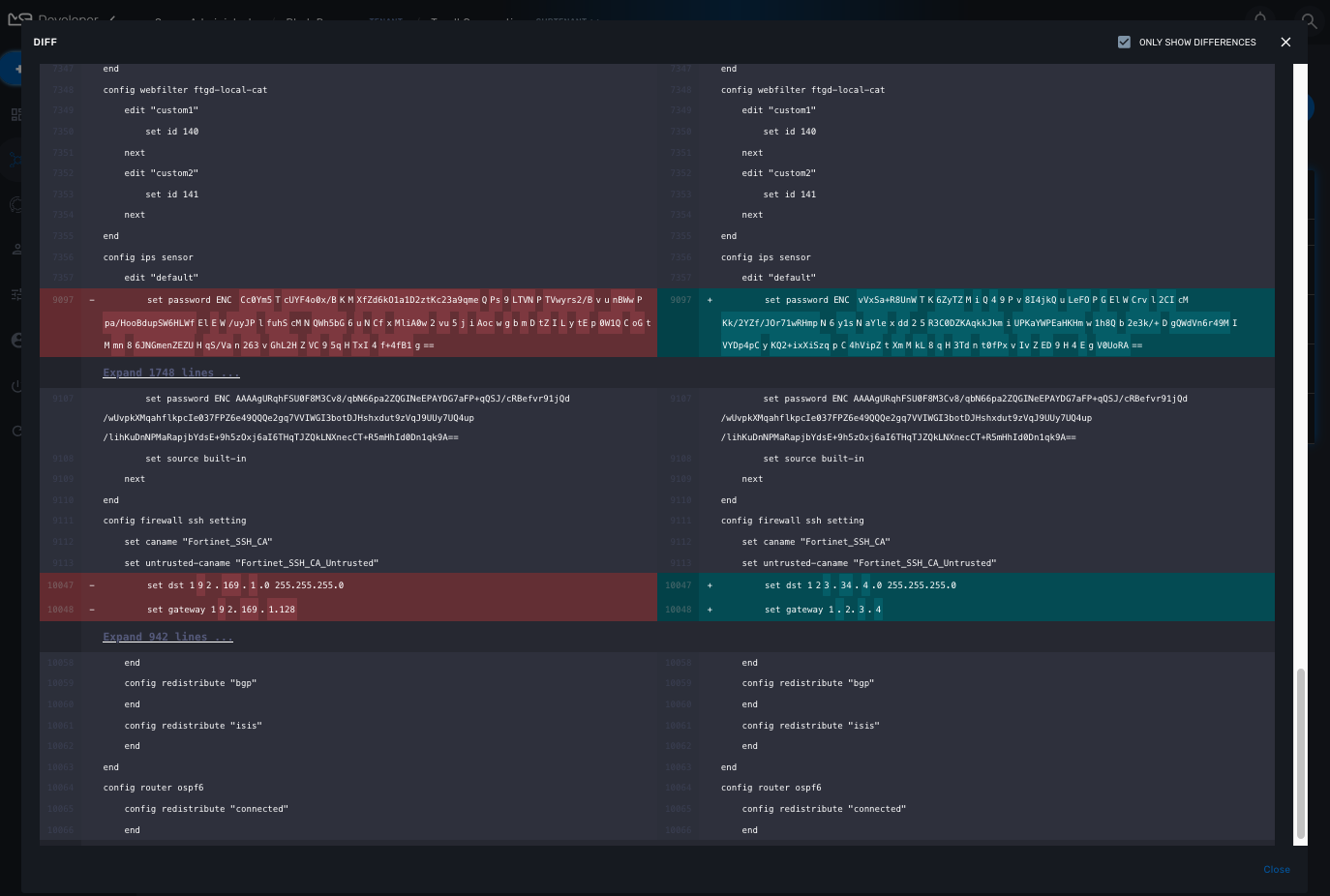
In the "History" tab of the managed entity, you will see the list of all configuration versions (revisions) available in the configuration database.
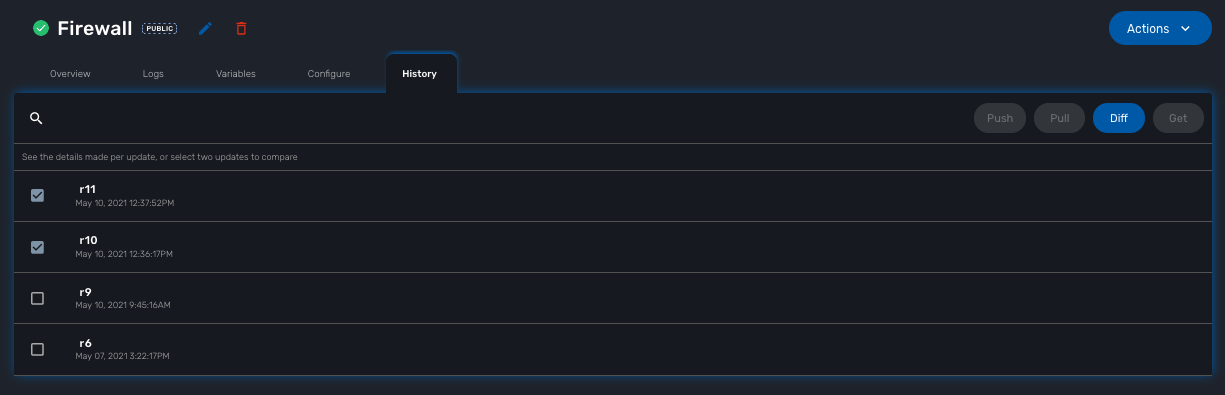
On this screen, you have the possibility to execute some action like restore a configuration (select a revision and use the Push button), backup a running configuration (use the Pull button) or display the differences between 2 selected revisions.